3D Secure
3DS (3D Secure) is an online payment authentication protocol that enhances anti-fraud efforts. It requires cardholders to undergo an additional layer of verification, such as a one-time password or biometric scan, during online transactions. This extra step helps verify the identity of the cardholder, reducing the risk of unauthorized payments, improving overall payment security, and allowing merchants to shift chargeback liability to the Issuing Bank.
Independent 3D Secure usage becomes crucial for various reasons, notably in the EU where it's mandated for all transactions. High-risk Merchant Category Codes (MCC) like gambling or adult entertainment may require 3DS authentication due to increased fraud potential. Additionally, an agnostic 3DS tool becomes essential for downstream decision-making when transaction settlement details are uncertain, requiring independence from PSP 3DS implementations
Basis Theory 3D Secure Integrations offers a range of options to integrate 3D Secure into any company's payment infrastructure, alleviating the need for extensive PCI Level 1 compliance. These integrations connect with our existing services, ensuring a streamlined interaction with any 3D Secure partner.
How to use 3D Secure with Basis Theory
Basis Theory Universal 3D Secure
Basis Theory's Universal 3D Secure ensures seamless integration with our Elements and can be employed against any processor or acquirer that accepts 3rd-party 3DS authorizations. Through the use of our Universal 3D Secure, companies can swiftly route transactions to any processor with a single integration.
To begin leveraging our Universal 3DS, visit our 3D Secure guides to initiate the integration process.
Processor or Acquirer 3D Secure
Basis Theory allows the flexibility to leverage any Processor's 3D-secure offerings. This empowers your engineers to integrate with processors like Stripe, Braintree, or Adyen's offering. Find more integration examples in our 3D Secure repository.
Standalone 3DS
Similar to utilizing a processor's 3DS solution, Basis Theory also enables standalone 3D Secure integrations by supporting various third-party providers like Cardinal Commerce, Ravelin, 3DSecure.io, and others. This flexibility empowers any team to choose the best-fit solution for their specific needs.
How does a company use 3D Secure?
There are two types of transaction flows that need to be accounted for when a company is looking to integrate 3D Secure into its system. The first is Customer Initiated Transaction which happens whenever a person is actively participating in a checkout process - for example, buying a product online. The second is a Merchant Initiated Transaction which happens when a customer is not active and the merchant is charging the credit card on their behalf - For example when paying for a monthly subscription.
Customer Initiated Transactions (CIT)
The first is a Customer Initiated Transaction (CIT), in this scenario, the customer is purchasing a good or service from your e-commerce solution.
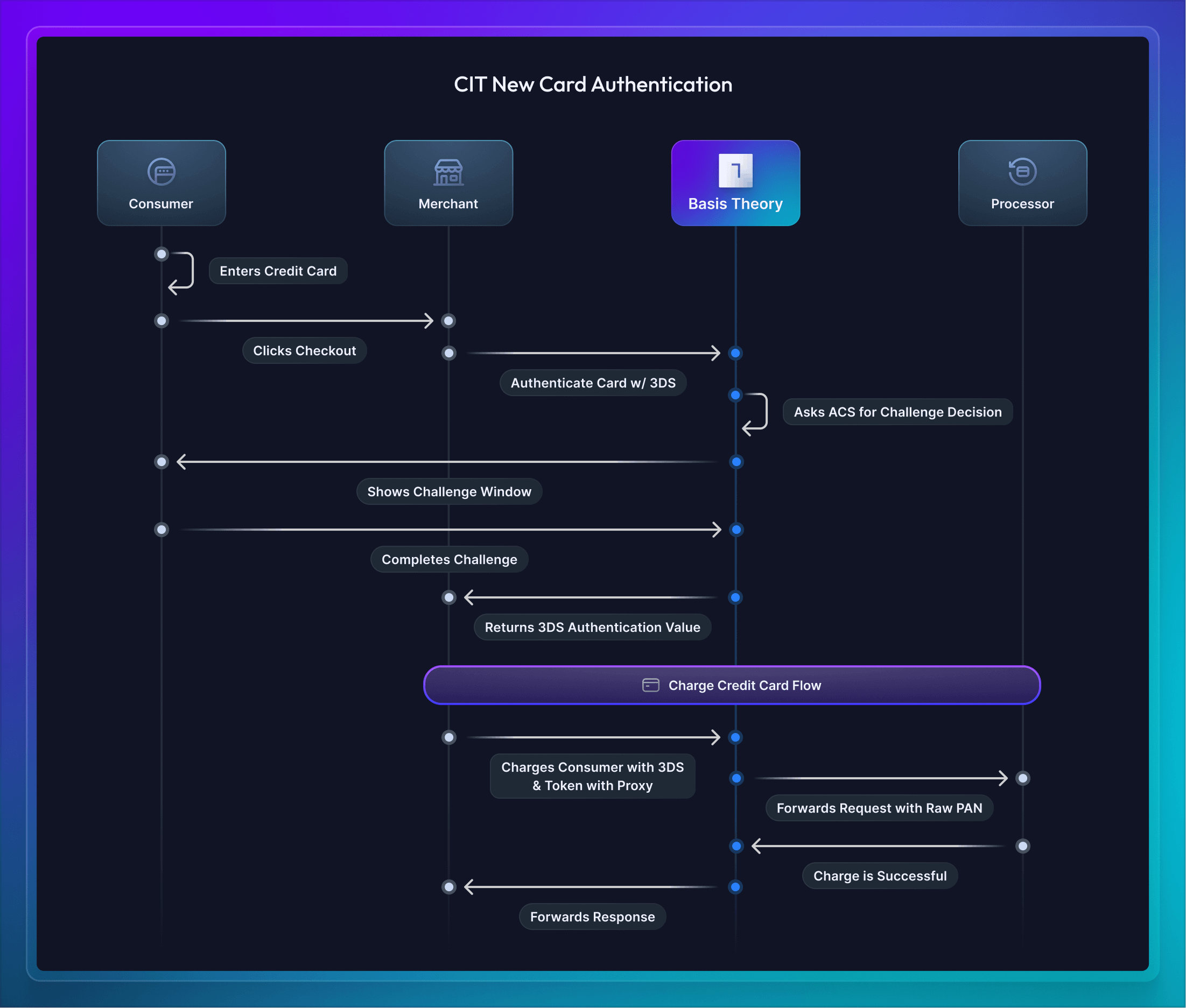
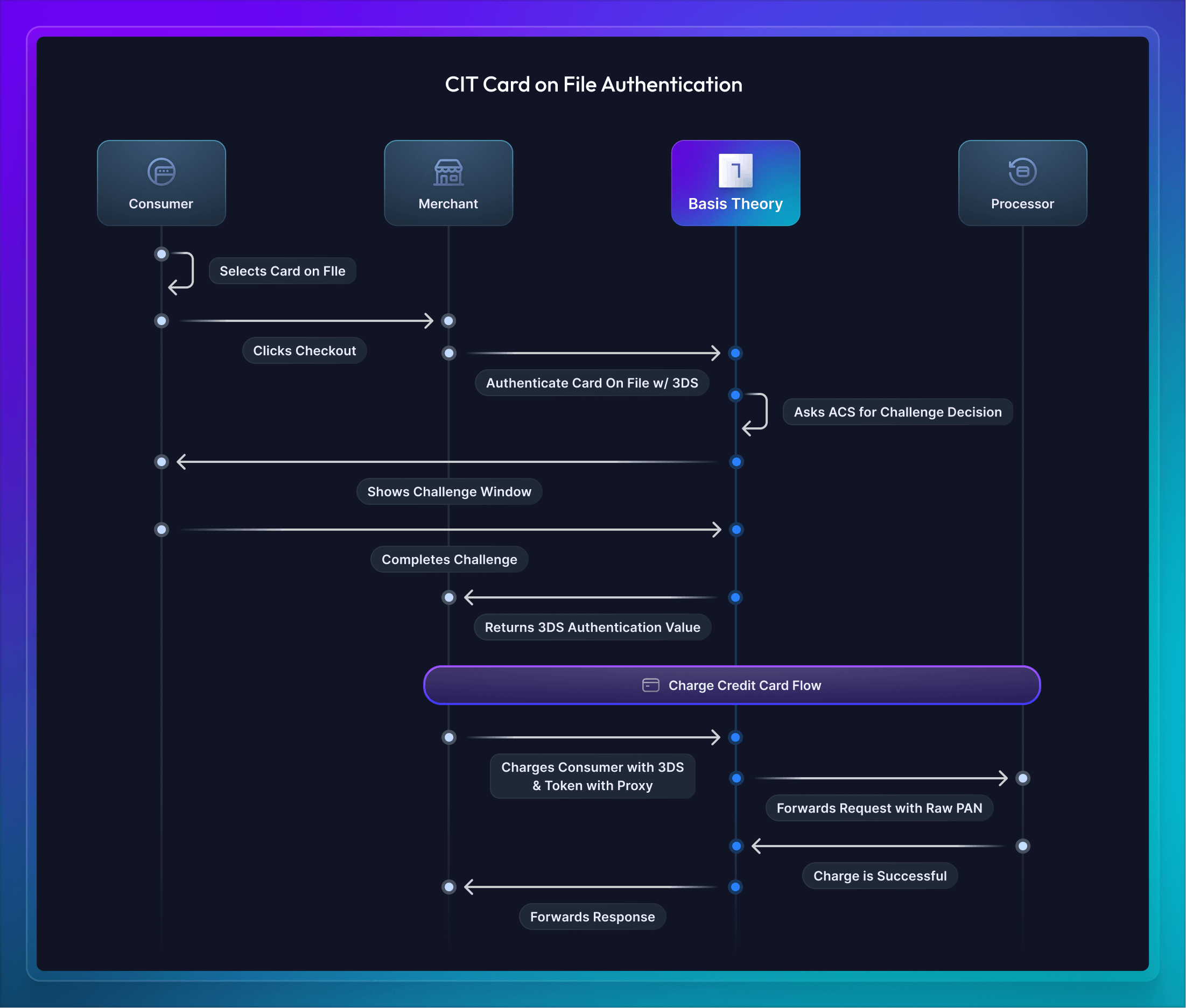
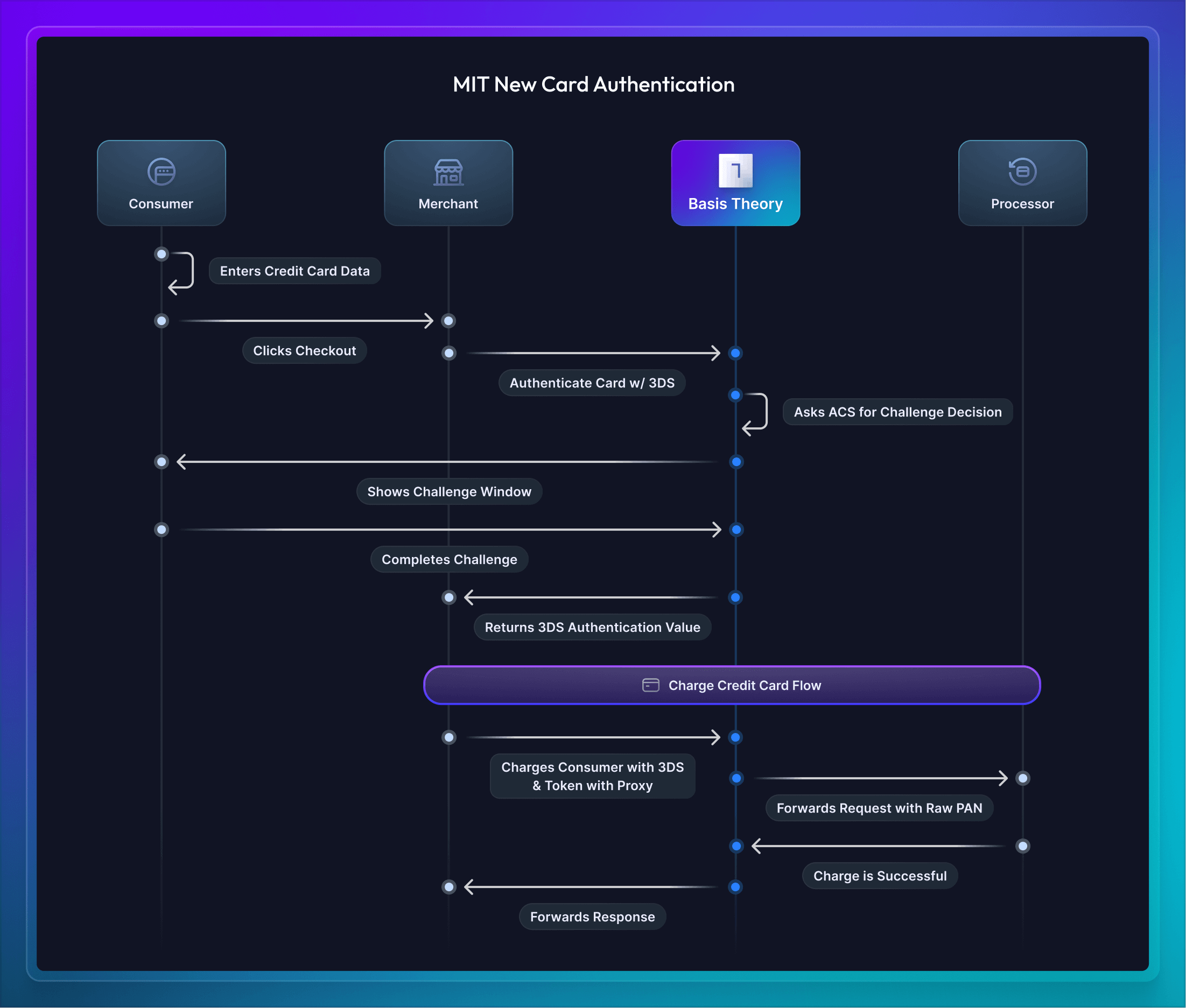
Once the credit card is entered by the Consumer, the company will authenticate the card with our Universal 3DS. Basis Theory will communicate with the Access Control Server (ACS) to determine if a challenge is required or frictionless authentication is possible. When a challenge is required, Basis Theory shows a window for the customer to verify with their bank (e.g., passwordless, username/password, etc). Finally, once the 3DS verification is complete an authorization token is returned and able to be forwarded along with a charge to the processor.
Merchant Initiated Transactions (MIT)
The second is a Merchant-initiated transaction when collecting a credit card for a subscription service and charging it each period after - in this scenario, 3DS is required to challenge the initial collection of the credit card, and each transaction after can be facilitated only between the merchant and Basis Theory.
Basis Theory Universal 3D Secure Enterprise
Basis Theory Universal 3D Secure can be used with or without Basis Theory's Elements, making it an excellent solution for any user experience a company is looking for. When utilizing Elements, using the Universal 3D Secure is as simple as a single authenticate call from within your UI - Basis Theory handles the rest.
Customer Initiated Transaction
When adding a new card
The first CIT use-case is when a company is initially collecting a credit card to use 3DS authentication and charge a customer. In this scenario, the merchant has implemented Basis Theory's Elements and the customer is typing their credit card number directly into the Element to pay for a product or service.
When using existing tokens
The second CIT use-case is when a customer's card is already on file and vaulted with Basis Theory. In this scenario, the merchant is able to use 3DS authentication and charge this card directly without asking the customer to re-type it in to purchase a product or service. In certain regions and to take advantage of the chargeback liability shift, this process is still required for card-on-file transactions when the customer is present during the transaction.
Merchant Initiated Transaction
When adding a new card to a subscription
The first use-case for MIT transactions is the initial capture of the credit card to use 3DS authentication and start a subscription. In this scenario, the merchant has implemented Basis Theory's Elements and the customer is typing their credit card number directly into the Element to start a subscription.
When using existing tokens
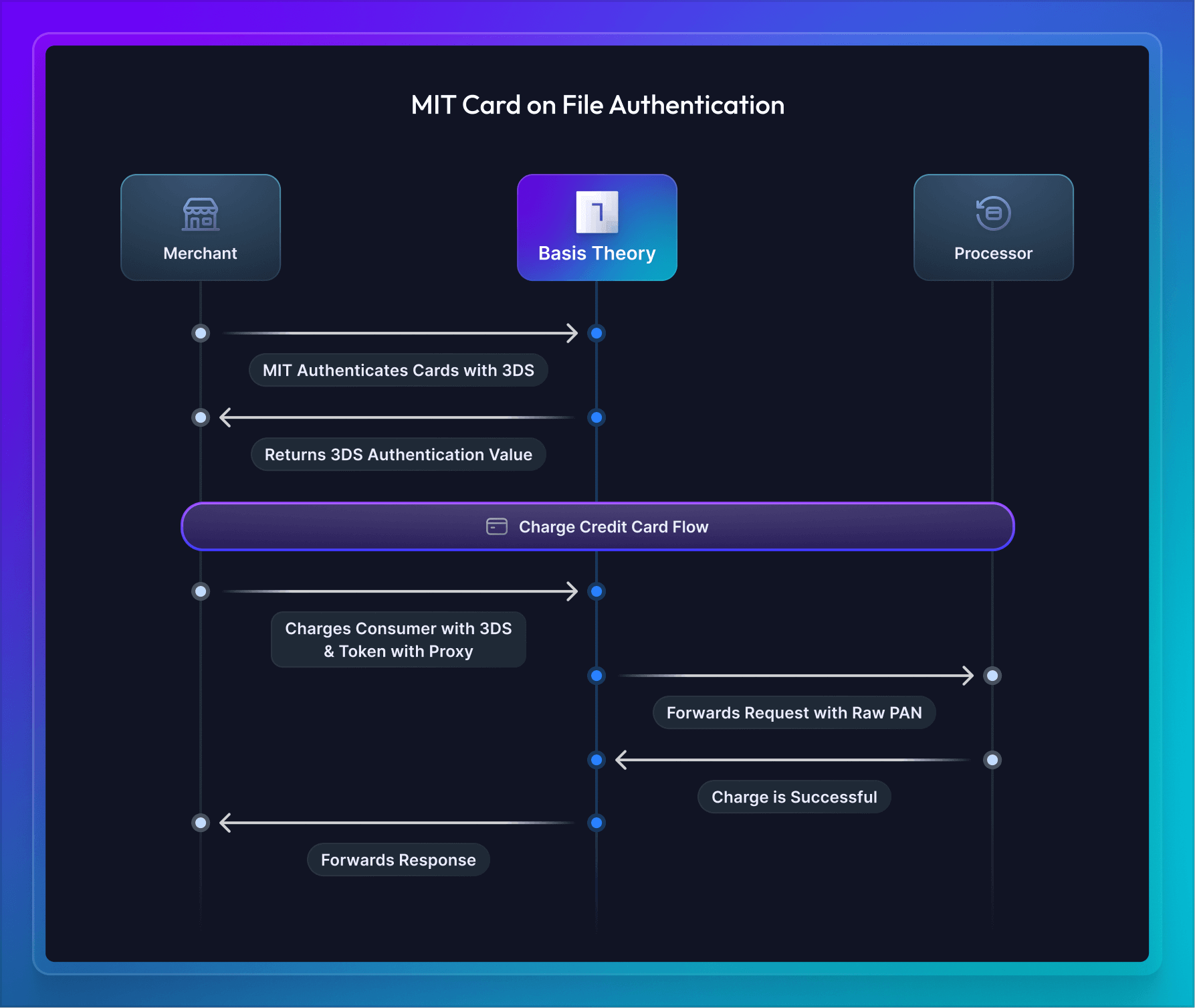
The second MIT use-case is when a customer's card is already on file and vaulted with Basis Theory. In this scenario, the merchant is able to use 3DS authentication and charge this card directly without asking the customer to re-type the card for a monthly subscription charge. In this scenario, a merchant's customer is not required to be challenged as they are not present during the transaction flow.
FAQ
Can we include a merchant's MID/BIN (acquirerId/acquirerBin) in the 3DS calls?
Yes. Companies are able to send any of their MIDs to the 3DS flow.
Does this 3DS implementation support using network tokens in the 3DS call rather than a PAN?
Yes. We provide the ability to send EMV Payment Tokens instead of PANs.
What is the Access Control Server (ACS)?
The Access Control Server (ACS) in the issuing bank's domain authenticates cardholders during transactions. Customers verify their identity through the ACS by providing information like passwords or codes, which the ACS checks against the issuing bank's data. The ACS, integral to customer authentication, plays a role in liability shifts for chargebacks to the issuing bank when merchants utilize 3DS.
Do you support frictionless authentication?
Yes. The ACS will evaluate risk associated with the transaction, cardholder data, collected device data, regulatory requirements and issuer's authentication policies to decide whether a frictionless authentication is possible or a challenge is necessary.
When frictionless authentication is achieved, the authentication value is returned automatically. When a challenge is required, the challenge window will pop up to the user. No decisioning logic is necessary from the merchant perspective.
What processors accept third-party 3DS?
These are known partners Basis Theory with the ability will accept a third-party 3DS token. If a processor does not exist in this list, we suggest working directly with the processor to ensure they are capable of accepting a 3DS authentication token.
- Adyen
- Airwallex
- Bambora North America (formerly Beanstream)
- BlueSnap
- Braintree
- CardConnect
- Cardstream
- Cecabank
- Checkout.com
- Credorax
- CyberSource
- dLocal
- Diamond Mind
- Global Payments
- iVeri
- Kushki
- MONEI
- Moneris
- NMI
- Orbital (Chase Paymentech)
- Payflow Pro
- Paymentez
- PayPal
- Paysafe
- Pin Payments
- Rapyd
- Nuvei (formerly SafeCharge)
- Shift4
- Worldline (formerly GlobalCollect)
- WorldPay