Anti-Fraud
The Basis Theory Platform allows businesses and payment service providers to easily connect with the anti-fraud solution that best suits their needs, helping them safeguard their operations and secure their financial transactions.
Risk assessment and Real-time decisioning
Transaction risk assessment involves a meticulous assessment of the potential risks associated with online transactions, particularly those involving credit cards. These solutions analyze various parameters, such as transaction history, user behavior, and device information, to identify patterns indicative of potential fraud.
Real-time decisioning anti-fraud solutions utilize advanced algorithms to assess transactions instantly, flagging suspicious activities in real-time. By leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning, these solutions can adapt and learn from evolving fraud tactics, enabling e-commerce businesses to make swift and well-informed decisions to prevent unauthorized transactions and protect both customers and the integrity of their digital platforms.
Together, these solutions create a robust defense mechanism, ensuring the security of online transactions in the dynamic landscape of e-commerce. The diagram below illustrates how merchants commonly integrate with anti-fraud risk assessment and decisioning systems, such as Forter, Sardine, and Kount, while leveraging the Basis Theory Platform to stay in control of their payment information.
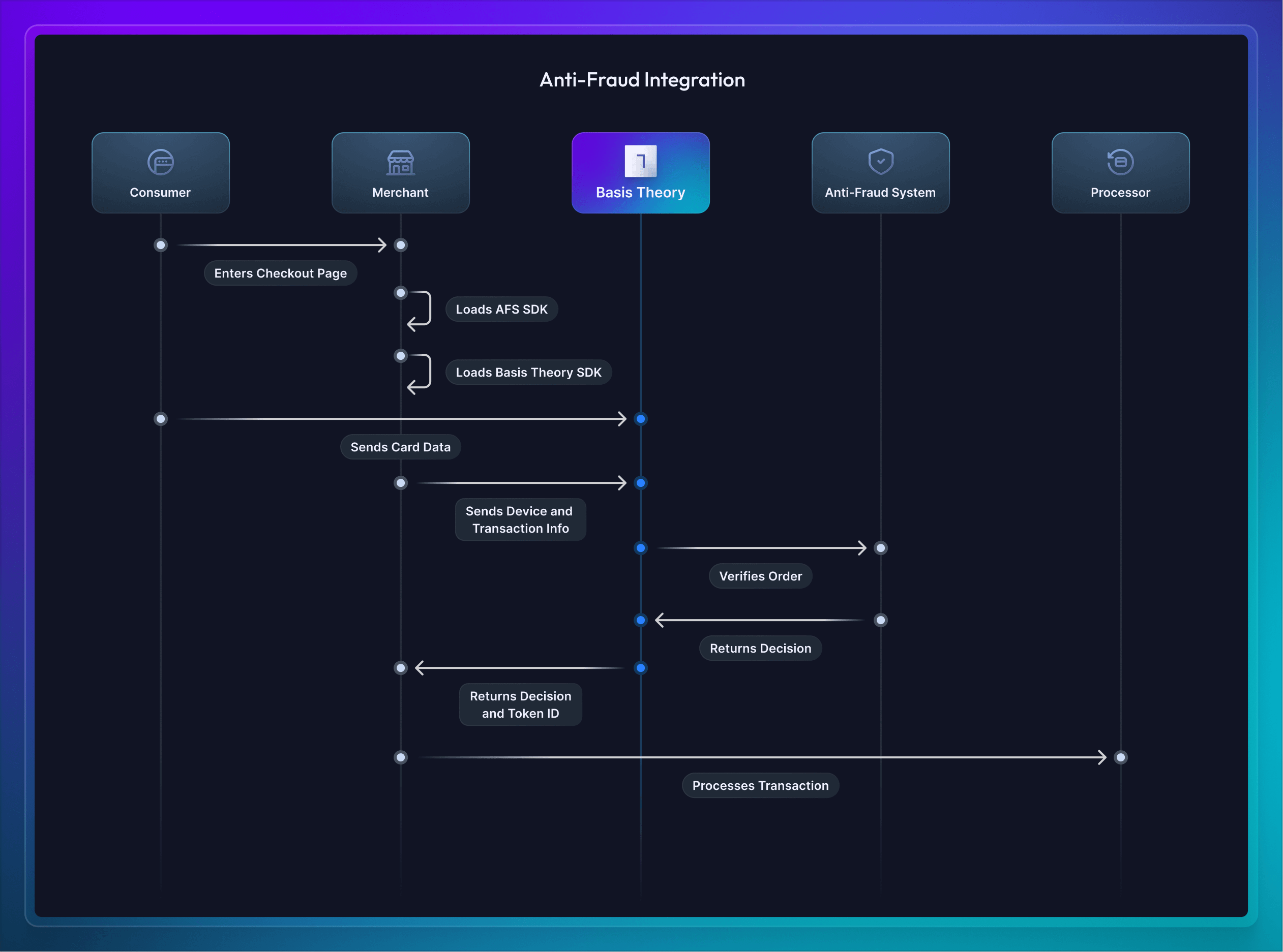
Device Fingerprinting
Device fingerprinting is a technique for identifying and tracking devices like smartphones, tablets, and computers based on their unique attributes and behaviors, which include device type, OS, browser version, screen resolution, and user behavior patterns.
Basis Theory Elements integrate with any device fingerprinting third-party by securely relaying API requests that contain bundled payloads. This allows passing vendor-generated device fingerprint information and/or identifier, and cardholder data through an isolated client maintained by Basis Theory.
Device fingerprinting is also automatically handled when using Basis Theory Universal 3D Secure.
Payment Verification Services
Payment Verification Services encompass a range of checks and validations designed to enhance transaction security and ensure the accuracy of payment information. These services vary among card networks and payment service providers, occurring at different stages within the payment processing workflow. Here are some examples:
- AVS (Address Verification Service) - During initial authorization: validate the cardholder's address against the billing address on file.
- Zero-Dollar Authorization - Early in the payment process: Pre-authorizes the card with a $0 transaction to verify its validity.
- Card Query - Various points in the process: Queries a card's details to confirm its existence and status.
- Card/Account Verification - During initial authorization: Verifies the authenticity of a credit card or bank account.
- Account Name Inquiry - During authorization: Validates cardholder names to prevent unauthorized transactions.
Such services will often rely on receiving a combination of Primary Account Number (PAN, aka the card number) with other customer information, such as name, billing address, card verification code, etc.
Use Basis Theory Elements to securely collect the cardholder data and bundle the payload to send the verification service:
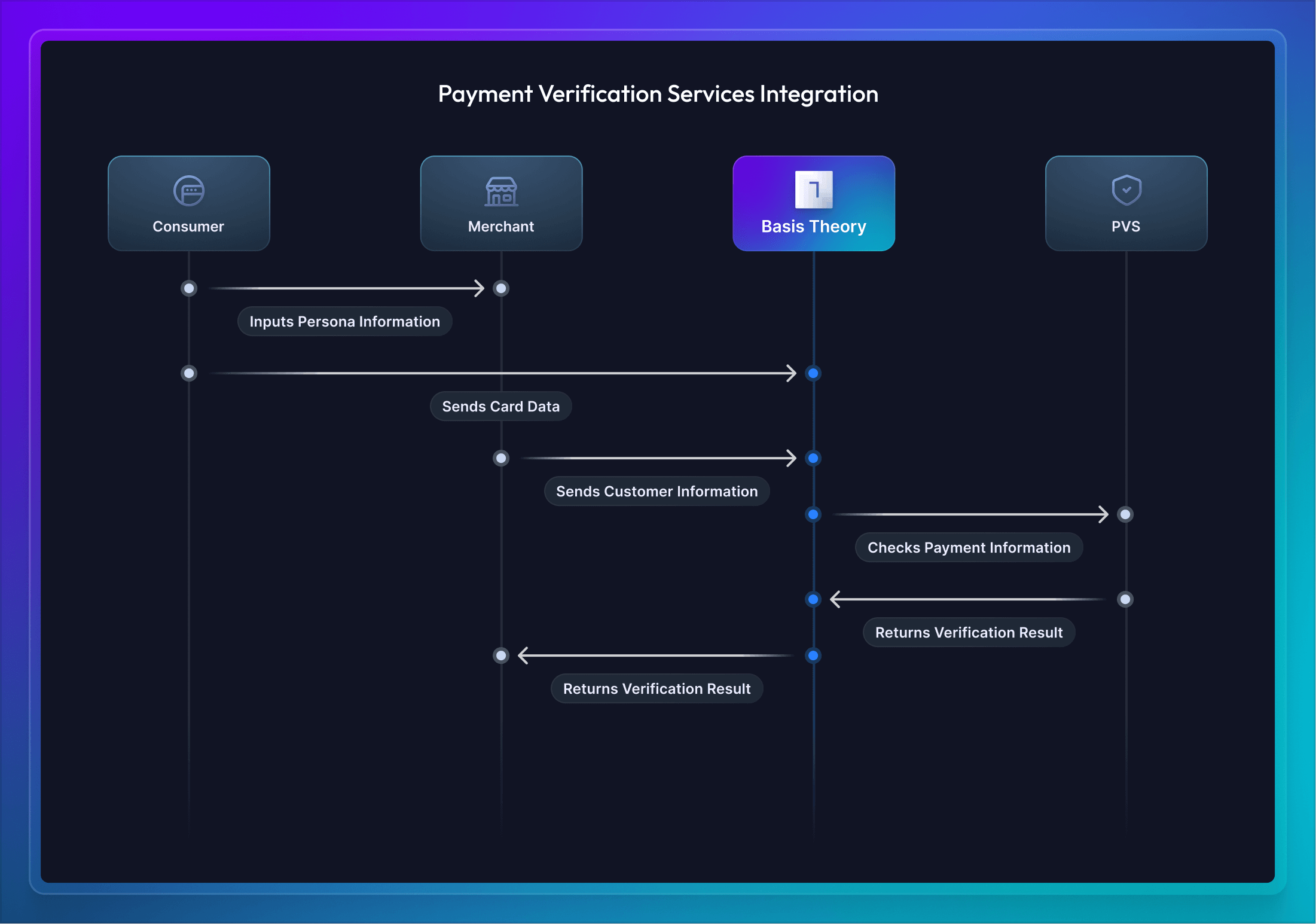
Card Fingerprinting
Card Fingerprinting, often referred to as “card hashing”, is a practice that involves converting sensitive credit card information, such as the card number and expiration date, into a unique, irreversible, and encrypted code or fingerprint.
Basis Theory Platform calculates a unique fingerprint during tokenization, which businesses and financial institutions can use to link together transactions made with the same card, even when used by different customers. This correlation enables the detection of unusual or suspicious patterns, such as a single credit card being used for an unusually high number of transactions across different accounts or geographic locations in a short timeframe.
3D Secure
3D Secure (3DS) is an online payment authentication protocol that enhances anti-fraud efforts. It requires cardholders to undergo an additional layer of verification, such as a one-time password or biometric scan, during online transactions. This extra step helps verify the cardholder's identity, reducing the risk of unauthorized payments, shifting chargeback liability away from the merchant, and improving overall payment security.
Visit our 3DS page to learn more about the different integration paths for 3D Secure.