3DS Implementation & Testing (CIT)
Customer Initiated Transactions (CIT) are 3DS transactions in which the customer is present during the transaction to complete any required external authorizations, such as a challenge.
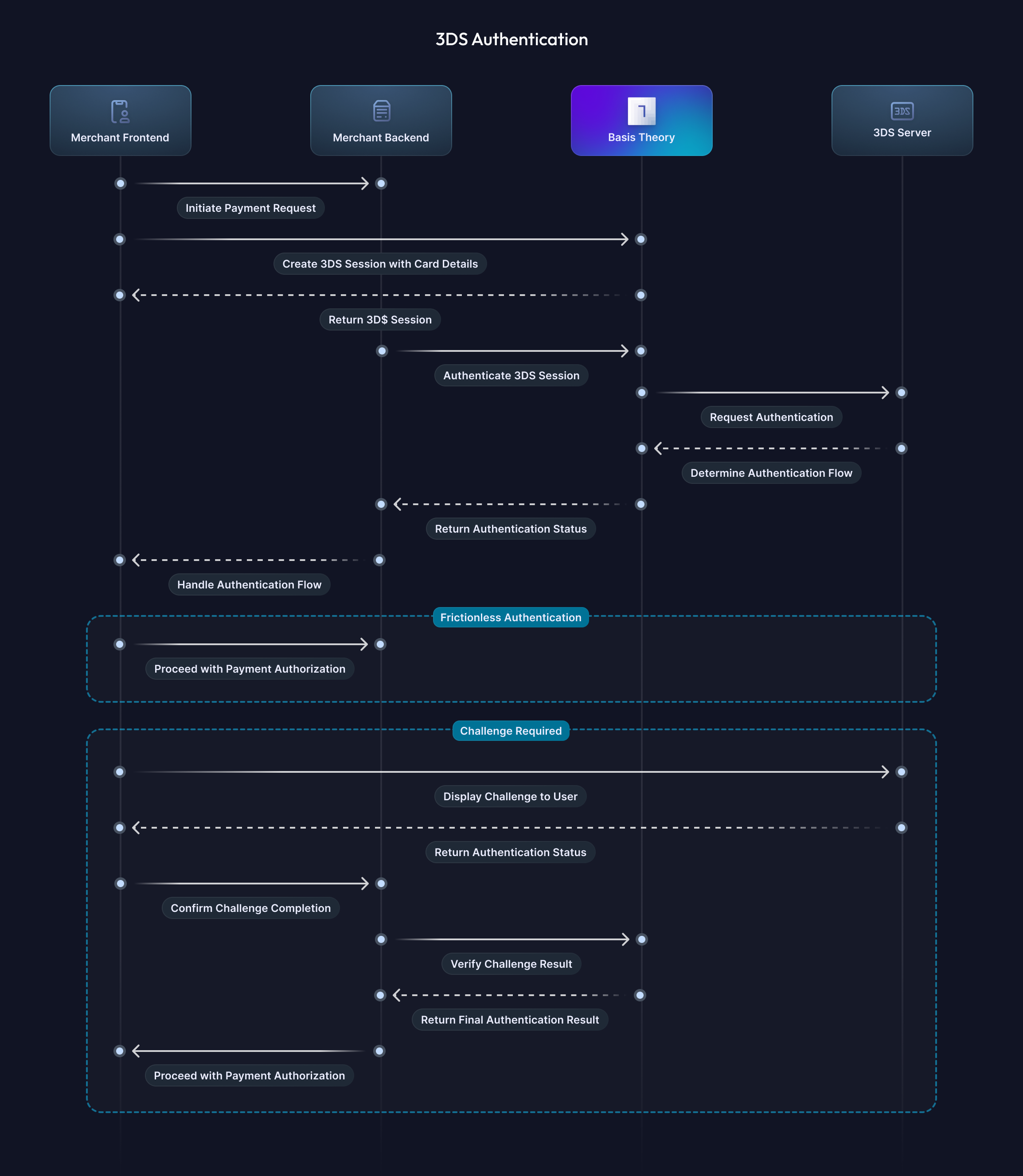
This guide covers the standard 3DS CIT implementation where the authentication flow is embedded directly in your checkout page using Basis Theory SDKs. If you prefer to redirect customers to the Basis Theory 3DS authentication page instead (and have to perform less steps), please refer to the 3DS CIT with Redirection guide.
If you perform transactions without the customer present at checkout, these are classified as Merchant-Initiated Transactions (MIT). For guidance on implementing 3DS MIT, please refer to the implementation guide here.
Summary
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of determining when 3D Secure (3DS) authentication is required, properly implementing the authentication flow, handling different challenge flows, and testing your implementation.
When is 3DS Required?
It is important to keep in mind every business has its own bespoke needs when it comes to risk, fraud, and compliance, and all of these variables impact its decision on how to best implement the 3DS authentication pattern for your business.
Triggering 3DS Considerations
Basis Theory simplifies this determination through the authentication field provided in the card token details object.
When this value is sca_required, this suggests the underlying Issuer will require 3DS to be present during the transaction.
While this could likely be true, there are a few considerations and scenarios to consider as you decide how to best optimize for triggering 3DS and optimizing Payment Authorization success:
- When a region always requires 3DS:
- Consider always triggering 3DS when
card.authenticationissca_requiredon your Token or Token Intent's card details object.
- Consider always triggering 3DS when
- When a region does not always require 3DS:
- Consider triggering the 3DS flow after a declined payment authorization to retry the transaction quickly while the customer is still engaged.
- When receiving inconsistent payment authorization declines for Authentication data:
- Consider triggering a frictionless only 3DS flow for these regions or BINs before Authorization. If a challenge is required, consider moving forward with your Authorization without the 3DS Authentication.
- Consider triggering the 3DS flow after a declined authorization to retry the transaction quickly while the customer is still engaged.
Regulatory Context
Note: Always verify regulatory requirements specific to your region and confirm with your PSP to ensure compliance and avoid declined transactions.
Certain regions typically mandate 3DS authentication, notably:
- European Economic Area (EEA)
- United Kingdom (UK)
- Other regions adopting Strong Customer Authentication (SCA): Australia, India, Brazil, and parts of Asia
Provisioning Resources
To successfully process 3DS authentications, you must first create two applications in the Basis Theory Portal: a Public Application and a Private Application. These applications will handle creating and authenticating 3DS sessions.
Public Application
The Public Application allows your front-end or client-side integration to create 3DS sessions securely.
- Permissions Required:
3ds:session:create
Click here to create the Public Application
Important: Save the generated API Key. You'll use it later in this guide.
Private Application
The Private Application is used by your backend system to authenticate the created 3DS sessions.
- Permissions Required:
3ds:session:authenticate
Click here to create the Private Application
Important: Save the generated API Key. You'll use it later in this guide.
Creating a CIT 3DS Session
The 3D Secure process starts by gathering information from the customer's device to verify transaction validity.
Creating a 3DS session with an existing card Token or Token Intent will automatically collect device information and attach it to the session.
The code examples below demonstrate how to create sessions using our available SDKs.
- Web
- React Native
- iOS
- Android
import { BasisTheory3ds } from "@basis-theory/web-threeds";
const authenticate = async () => {
const bt3ds = BasisTheory3ds("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>");
// creating the session
// (in this example we are using tokenId for a card token, use tokenIntentId for a token intent)
const session = await bt3ds.createSession({ tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>" });
}
import { BasisTheory3dsProvider, useBasisTheory3ds } from "@basis-theory/react-native-threeds";
const App = () => {
return (
<BasisTheory3dsProvider apiKey={"<PUBLIC_API_KEY>"}>
<MyApp />
</BasisTheory3dsProvider>
);
}
const MyApp = () => {
const { createSession, startChallenge } = useBasisTheory3ds();
// higlight-start
//creating the session
// (in this example we are using tokenId for a card token, use tokenIntentId for a token intent)
const session = await createSession({ tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>" });
}
import ThreeDS
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, UITextFieldDelegate {
private var threeDSService: ThreeDSService!
private var sessionId: String? = nil
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
do {
threeDSService = try ThreeDSService.builder()
.withApiKey("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>")
.withAuthenticationEndpoint("<YOUR_BACKEND_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT>", headers: ["Header-Name": "value"])
.build()
Task {
try await threeDSService.initialize { [weak self] warnings in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
if let warnings = warnings, !warnings.isEmpty {
let messages = warnings.map { $0.message }.joined(separator: "\n")
print(messages)
} else {
print("3DS SDK initialized successfully.")
}
}
}
}
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
// call this method from your app when you want to create a session
@objc func createThreeDsSession() {
Task {
do {
// (in this example we are using tokenId for a card token, use tokenIntentId for a token intent)
let session = try await self.threeDSService.createSession(tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>")
sessionId = session.id
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
}
}
// ... other imports
import com.basistheory.threeds.service.ThreeDSService
import com.basistheory.threeds.model.CreateThreeDsSessionResponse
open class ThreeDsViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
private val _errorMessage = MutableLiveData<String?>(null)
val errorMessage: LiveData<String?> = _errorMessage
val session = MutableLiveData<CreateThreeDsSessionResponse?>(null)
private val threeDsService = ThreeDSService
.Builder()
.withApiKey("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>")
.withAuthenticationEndpoint("<YOUR_BACKEND_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT>")
.withApplicationContext(application.applicationContext)
.build()
fun initialize(): LiveData<List<String>> = liveData {
try {
val warnings = threeDsService.initialize()
if (!warnings.isNullOrEmpty()) {
emit(warnings.map { it.message })
} else {
emit(emptyList())
}
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(emptyList())
}
}
fun createSession(tokenId: String): LiveData<CreateThreeDsSessionResponse?> = liveData {
try {
session.value = threeDsService.createSession(tokenId = tokenId)
emit(session.value)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(null)
}
}
private fun onChallengeCompleted(result: ChallengeResponse) {
challengeResponse.postValue(result)
status.postValue(result.status)
result.details?.let {
statusReason.postValue(it)
}
}
private fun onChallengeFailed(result: ChallengeResponse) {
_errorMessage.postValue(result.toString())
}
fun startChallenge(sessionId: String, activity: Activity): LiveData<Boolean> = liveData {
_errorMessage.value = null
try {
threeDsService.startChallenge(
sessionId = sessionId,
activity = activity,
onCompleted = ::onChallengeCompleted,
onFailed = ::onChallengeFailed
)
emit(true)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(false)
}
}
}
3DS sessions that are not authenticated will expire according to the token or token-intent's designated expiration date.
If no expiration date is set, the session expires after one hour. Once a session is successfully authenticated, it remains active indefinitely.
Co-Badged Cards in 3DS Sessions
Co-badged cards are payment cards associated with multiple card networks or brands. For example, a single card might be accepted as both Visa and Cartes Bancaires.
When creating a 3DS session with a co-badged card, the response will include the additionalCardBrands property containing an array of all brands the card identifies with.
{
"id": "e4de227e-b71a-450e-87a1-ed9fbbc57aaf",
"cardBrand": "Visa",
"additionalCardBrands": ["Visa", "Cartes Bancaires"]
}
After receiving this information, you can choose which brand's authentication rails to use during the authentication step.
Authenticating a CIT 3DS Session
Authenticating a 3DS session will initialize the process with the Issuing Banks to coordinate information and determine the level of authentication required for a specific session. This authentication process will either determine if a session will require a Challenge (2-factor authentication) or will be authenticated Frictionless (not requiring a challenge).
It is the accepted practice that the more information you provide to a 3DS session, the higher the likelihood of a frictionless authentication.
This section will outline all the required fields for your specific transaction type.
Making a 3DS Authentication Request
This is the recommended minimum payload required for successful 3DS authentications in most scenarios:
{
"authentication_category": "payment",
"authentication_type": "payment-transaction",
"challenge_preference": "no-challenge", // or challenge-requested if challenge is preferred (not guaranteed).
"card_brand": "Visa", // optional for co-badged cards
"merchant_info": {
"mid": "9876543210001",
"acquirer_bin": "000000999",
"name": "Example 3DS Merchant",
"country_code": "7922",
"category_code": "826",
"url": "https://example.com",
},
"requestor_info": { // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
"amex_requestor_type": "MER", // if American Express is accepted
"cb_siret_number": "78467169500087", // If Cartes Bancaires is accepted
},
"purchase_info": {
"amount": "80000",
"currency": "826",
"exponent": "2",
"date": "20250101141010",
"transaction_type": "purchase",
"installment_count": "5", // only for installment transactions
"recurring_expiration": "20250131", // only for recurring transactions
"recurring_frequency": "30", // only for recurring transactions
},
"cardholder_info": {
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.com",
}
}
And below is how you can use this object to authenticate a 3DS session with the Basis Theory API and SDKs:
- cURL
- Node
- .NET
- Python
- Go
curl "https://api.test.basistheory.com/3ds/sessions/<SESSION_ID>/authenticate" \
-H "BT-API-KEY: <PRIVATE_API_KEY>" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-X "POST" \
-d '{
"authentication_category": "payment",
"authentication_type": "payment-transaction",
"challenge_preference": "no-challenge",
"card_brand": "Visa",
"merchant_info": {
"mid": "9876543210001",
"acquirer_bin": "000000999",
"name": "Example 3DS Merchant",
"category_code": "7922",
"country_code": "826",
"url": "https://example.com"
},
"requestor_info": {
"amex_requestor_type": "MER",
"cb_siret_number": "78467169500087"
},
"purchase_info": {
"amount": "80000",
"currency": "826",
"exponent": "2",
"date": "20240109141010",
"transaction_type": "purchase"
},
"cardholder_info": {
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.com"
}
}'
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK and Express framework for Node.js.
const express = require("express");
const { BasisTheoryClient } = require("@basis-theory/node-sdk")
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.use(express.json());
let bt;
(async () => {
// initialize the SDK
bt = await new BasisTheoryClient({ apiKey: "<PRIVATE_API_KEY>", environment: BasisTheoryEnvironment.Test });
// start the server (after SDK is initialized so we don't drop any requests
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
})();
app.post("/:sessionId/authenticate", async (req, res) => {
const { sessionId } = req.params;
try {
const authentication = await bt.threeds.sessions.authenticate(sessionId, {
authenticationCategory: "payment",
authenticationType: "payment-transaction",
challengePreference: "no-challenge",
// cardBrand: "Visa", // optional - used if co-badged card
merchantInfo: {
mid: "9876543210001",
acquirerBin: "000000999",
name: "Example 3DS Merchant",
categoryCode: "7922",
countryCode: "826",
url: "https://example.com",
},
requestorInfo: { // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
amexRequestorType: "MER", // if American Express is accepted
cbSiretNumber: "78467169500087", // if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
},
purchaseInfo: {
amount: "80000",
currency: "826",
exponent: "2",
date: "20240109141010",
transactionType: "purchase",
//installmentCount": "5", // only for installment transactions
//recurringExpiration: "20250131", // only for recurring transactions
//recurringFrequency: "30", // only for recurring transactions
},
cardholderInfo: {
name: "John Doe",
email: "john@example.com"
}
});
res.status(200).send(authentication);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error during authentication:', error);
res.status(500).send({ error: "Internal Server Error" });
}
});
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK and ASP.NET Core Framework.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BasisTheory.Client;
using BasisTheory.Client.Threeds;
namespace server.Controllers
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseUrls("http://0.0.0.0:4242")
.UseWebRoot("public")
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.Build()
.Run();
}
}
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().AddNewtonsoftJson();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment()) app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => endpoints.MapControllers());
}
}
[ApiController]
public class ThreeDsApiController : Controller
{
private readonly BasisTheory _client;
public ThreeDsApiController()
{
_client = new BasisTheory(apiKey: "<PRIVATE_API_KEY>");
}
[HttpPost("{sessionId:guid}/authenticate")]
public async Task<ActionResult> AuthenticateSession([FromRoute] Guid sessionId)
{
try
{
var authentication = await _client.Threeds.Sessions.AuthenticateAsync(sessionId.ToString(), new AuthenticateThreeDsSessionRequest
{
AuthenticationCategory = "payment",
AuthenticationType = "payment-transaction",
ChallengePreference = "no-challenge",
// CardBrand = "Visa", // optional - used if co-badged card
MerchantInfo = new ThreeDsMerchantInfo
{
Mid = "9876543210001",
AcquirerBin = "000000999",
Name = "Example 3DS Merchant",
CategoryCode = "7922",
CountryCode = "826",
Url = "https://example.com"
},
RequestorInfo = new ThreeDsRequestorInfo // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
{
AmexRequestorType = "MER", // if American Express is accepted
CbSiretNumber = "78467169500087" // if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
},
PurchaseInfo = new ThreeDsPurchaseInfo
{
Amount = "80000",
Currency = "826",
Exponent = "2",
Date = "20240109141010",
TransactionType = "purchase",
// InstallmentCount = "5", // only for installment transactions
// RecurringExpiration = "20250131", // only for recurring transactions
// RecurringFrequency = "30", // only for recurring transactions
},
CardholderInfo = new ThreeDsCardholderInfo
{
Name = "John Doe",
Email = "john@example.com"
}
});
if (authentication == null)
{
return Problem("Error during authentication.");
}
return Ok(authentication);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error during authentication: {ex.Message}");
return Problem("Internal Server Error");
}
}
}
}
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK and Flask Framework.
import os
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from basis_theory import (
BasisTheory,
ThreeDsMerchantInfo,
ThreeDsRequestorInfo,
ThreeDsPurchaseInfo,
ThreeDsCardholderInfo
)
app = Flask(__name__)
client = BasisTheory(api_key="<PRIVATE_API_KEY>")
@app.route('/<sessionId>/authenticate', methods=['POST'])
def authenticate_session(sessionId):
authentication = client.threeds.sessions.authenticate(
session_id=sessionId,
authentication_category="payment",
authentication_type="payment-transaction",
challenge_preference="no-challenge",
# card_brand="Visa", # optional - used if co-badged card
merchant_info=ThreeDsMerchantInfo(
mid="9876543210001",
acquirer_bin="000000999",
name="Example 3DS Merchant",
category_code="7922",
country_code="826",
url="https://example.com"
),
requestor_info=ThreeDsRequestorInfo( # if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
amex_requestor_type="MER", # if American Express is accepted
cb_siret_number="78467169500087" # if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
),
purchase_info=ThreeDsPurchaseInfo(
amount="80000",
currency="826",
exponent="2",
date="20240109141010",
transaction_type="purchase",
# installment_count="5", # only for installment transactions
# recurring_expiration="20250131", # only for recurring transactions
# recurring_frequency="30", # only for recurring transactions
),
cardholder_info=ThreeDsCardholderInfo(
name="John Doe",
email="john@example.com"
)
)
if authentication is None:
return jsonify({"error": "Error during authentication."}), 500
return jsonify(authentication.to_dict()), 200
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(port=4242, debug=True)
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK, Go HTTP package and the Gorilla Mux Router.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk"
basistheoryclient "github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/client"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/option"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/threeds"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
"log"
"net/http"
)
var client *basistheoryclient.Client
func main() {
client := basistheoryclient.NewClient(
option.WithAPIKey("<API_KEY>"),
)
router := mux.NewRouter()
router.HandleFunc("/{sessionId}/authenticate", authenticateSession).Methods("POST")
addr := "localhost:4242"
log.Printf("Listening on %s", addr)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(addr, router))
}
func pointerToString(s string) *string {
return &s
}
func authenticateSession(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
sessionId := vars["sessionId"]
authRequest := &threeds.AuthenticateThreeDsSessionRequest{
AuthenticationCategory: pointerToString("payment"),
AuthenticationType: pointerToString("payment-transaction"),
ChallengePreference: pointerToString("no-challenge"),
// CardBrand: pointerToString("Visa"), // optional - used if co-badged card
}
merchantInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsMerchantInfo{
Mid: pointerToString("9876543210001"),
AcquirerBin: pointerToString("000000999"),
Name: pointerToString("Example 3DS Merchant"),
CategoryCode: pointerToString("7922"),
CountryCode: pointerToString("826"),
Url: pointerToString("https://example.com"),
}
requestorInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsRequestorInfo{ // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
AmexRequestorType: pointerToString("MER"), // if American Express is accepted
CbSiretNumber: pointerToString("78467169500087"), // if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
}
purchaseInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsPurchaseInfo{
Amount: pointerToString("80000"),
Currency: pointerToString("826"),
Exponent: pointerToString("2"),
Date: pointerToString("20240109141010"),
TransactionType: pointerToString("purchase"),
// InstallmentCount: pointerToString("5"), // only for installment transactions
// RecurringExpiration: pointerToString("20250131"), // only for recurring transactions
// RecurringFrequency: pointerToString("30"), // only for recurring transactions
}
cardholderInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsCardholderInfo{
Name: pointerToString("John Doe"),
Email: pointerToString("john@example.com"),
}
authRequest.MerchantInfo = merchantInfo
authRequest.RequestorInfo = requestorInfo
authRequest.PurchaseInfo = purchaseInfo
authRequest.CardholderInfo = cardholderInfo
authenticateResponse, authenticateErr := client.Threeds.Sessions.Authenticate(context.Background(), sessionId, authRequest)
if authenticateErr != nil {
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
json.NewEncoder(rw).Encode(map[string]string{"error": authenticateErr.Error()})
return
}
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
json.NewEncoder(rw).Encode(authenticateResponse)
}
After authenticating, you'll receive an Authentication Response object, for which an example can be found below:
{
"pan_token_id": "ac7bade2-fe34-4194-aa86-13771b32fbef",
"token_id": "ac7bade2-fe34-4194-aa86-13771b32fbef",
"session_id": "e4de227e-b71a-450e-87a1-ed9fbbc57aaf",
"threeds_version": "2.2.0",
"acs_transaction_id": "ccfe56b0-2d38-414b-8a13-a7c1a6d13aa5",
"ds_transaction_id": "beb1370a-64ca-4988-8ac5-dd81ca2d77ea",
"acs_reference_number": "mock-acs-reference-number",
"ds_reference_number": "mock-directory-server-a",
"liability_shifted": false,
"authentication_value": "LVJhdmVsaW4gVGVzdCBWYWx1ZS0=",
"authentication_status": "successful",
"authentication_status_code": "Y",
"directory_status_code": "Y",
"eci": "05",
"challenge_preference": "no-challenge",
"challenge_preference_code": "02"
}
More information on how to handle the Authentication Response can be found here.
Continue reading to learn more about each property in the Authentication Request object and how to best utilize them for your specific use case.
Authentication Request Property Details
Authentication Category
For the authentication_category field, there are two authentication categories available - In most 3DS scenarios, you'll select the payment category, indicating that a current or future financial transaction (including $0 authentications) is intended.
| Authentication Category | Description |
|---|---|
payment | Utilized when a future financial transaction is intended (including $0 authentications). |
non-payment | Utilized when the authentication is unrelated to an actual or anticipated charge. If you believe you need to utilize this category, please reach out to confirm your use-case. |
Authentication Type
For the authentication_type field, there are three most common types available. The below table outlines the common scenarios for most merchants and platforms:
| Authentication Type | Description |
|---|---|
payment-transaction | Used for a single exchange of goods (e.g. E-commerce checkout) |
recurring-transaction | Used for on-going subscriptions where the billed amount is always the same. (e.g. Monthly Subscription) |
installment-transaction | Used for breaking a single purchase into multiple installments. (e.g. Buy Now Pay Later) |
If your use case does not align with these options, please contact us at support@basistheory.com to discuss what you should select.
Merchant Information
Merchant information allows the issuer and 3DS server to accurately identify your business during authentication. Correctly configuring these details is essential to prevent authentication failures.
Below is a detailed explanation of each merchant information field and guidelines for populating them.
You should have received these values from your Payment Service Provider (PSP) during the 3DS Setup process. If you have questions or haven't received the values for these fields, please contact your PSP and let them know that you need these details for each card network/brand you accept - a request template can be found here.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
mid | A unique identifier assigned by your PSP to identify your merchant account. |
acquirer_bin | Unique numeric identifier assigned to the PSP by each card network/brand. |
name | The official business name associated with your PSP merchant account. |
country_code | Numeric code representing merchant's country location (ISO 3166-1 standard). |
category_code | A four-digit number assigned by your PSP indicating your type of business. Also known as MCC. |
url | Business URL for the merchant. |
Merchant information often varies depending on the card network or brand. You must implement logic within your application to dynamically select the appropriate values based on the card network or brand used for each transaction.
Merchant Information Example Object
"merchant_info": {
"mid": "9876543210001",
"acquirer_bin": "000000999",
"name": "Example 3DS Merchant",
"country_code": "7922",
"category_code": "826",
"url": "https://example.com",
}
Requestor Information for AMEX, Discover, Cartes Bancaires
American Express, Discover, and Cartes Bancaires (all supported by Basis Theory 3DS) require special 3DS Requestor information in addition to the standard Merchant Information.
If you accept payments from these networks, you should have received the necessary 3DS Requestor Information from your Payment Service Provider (PSP), as outlined in our 3DS Setup Guide.
If any details are missing or unclear, please contact your PSP directly, clearly communicating the specific data points required according to the setup guide - a request template can be found here.
Requestor Information for American Express (AMEX)
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
amex_requestor_type | Defines the merchant type according to American Express requirements. For most cases, we recommend using MER, which represents a general merchant. If your business operates as an aggregator, an online travel agency, or you're unsure whether MER applies to your scenario, refer to the 3DS Setup Guide for alternative values and guidance. |
Requestor Information for Cartes Bancaires
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
cb_siret_number | 14-digit code that identifies a business establishment in France. |
Requestor Information for Discover
Discover cards, predominantly issued by U.S. banks, rarely require Strong Customer Authentication (SCA).
If you need support for Discover 3DS authentication, please reach out via support@basistheory.com.
Requestor Information Example Object
To simplify implementations - these requestor fields may be included in every request regardless of the brand. Basis Theory automatically handles these values internally, using only those relevant to the card network involved in each transaction.
"requestor_info": {
"amex_requestor_type": "MER", // if American Express is accepted
"cb_siret_number": "78467169500087", // If Cartes Bancaires is accepted, replace with your real SIRET number
}
Purchase Information
It is essential to provide accurate details about the transaction to ensure successful authentication; if you believe you do not need to provide these values, please reach out.
The information below is recommended for all 3DS authentications regardless of the Authentication Type selected.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
amount | The purchase amount without any punctuation (i.e. 80000 for 800.00). |
currency | The purchase currency code in ISO 4127 standard. |
exponent | The minor units of currency as in the ISO 4127 standard. |
date | The purchase date in UTC timezone and YYYYMMDDhhmmss format. |
transaction_type | Specifies the type of transaction being authenticated. For most use cases, we recommend using purchase. If your transaction falls under special scenarios, such as check acceptance or other uncommon types, refer to our API Reference for additional values and their descriptions. |
Recurring Purchase
The following properties are required to be provided if your Authentication Type is set to recurring-transaction
Beyond the initial CIT authentication - Most recurring transactions or installments are exempt from 3DS authentication. However, the best practice is to verify with your PSP whether additional authentication exemptions or requirements apply to your recurring or installment transactions.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
recurring_expiration | Final recurring authorization date in YYYYMMDD format. |
recurring_frequency | Number of days between recurring charges. |
Installment Purchase
The following property is required to be provided if your Authentication Type is set to installment-transaction
Beyond the initial CIT authentication - Most recurring transactions or installments are exempt from 3DS authentication. However, the best practice is to verify with your PSP whether additional authentication exemptions or requirements apply to your recurring or installment transactions.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
installment_count | Total number of installments for installment payments. |
Purchase Information Example Object
"purchase_info": {
"amount": "80000",
"currency": "826",
"exponent": "2",
"date": "20250101141010"
"transaction_type": "purchase",
// only for installment transactions
"installment_count": "5",
// only for recurring transactions
"recurring_expiration": "20250131",
"recurring_frequency": "30",
}
Cardholder Information
Card networks strongly recommend including detailed cardholder information alongside transaction details to improve the likelihood of frictionless authentication.
As a general rule, providing more comprehensive information increases the effectiveness of the 3DS authentication process.
The fields below are, at a minimum, what most card networks require:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
name | The full name of the cardholder full name. |
email | The email address on-file for the cardholder |
Cardholder Information Example Object
"cardholder_info": {
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "john@example.com",
}
(Optional) Challenge Preference
For the challenge_preference field, the two most common values are available to instruct the issuer of the authentication preference. The table below outlines the common scenarios for most merchants and platforms:
Note: This preference is treated as a suggestion to the issuer and there is no guarantee it will be honored, as the final decision remains at the issuer's discretion.
| Challenge Preference | Description |
|---|---|
no-challenge | Used when preference for a frictionless authentication, to minimize friction by avoiding authentication challenges. |
challenge-requested | Used when explicitly requiring a challenge for the transaction - typically used if you suspect fraud. |
To see more challenge preference options and related EMV codes, refer to our API Reference.
(Optional) Card Brand Selection
For co-badged cards (cards associated with multiple card networks), you can specify which card brand to use for authentication:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
card_brand | The specific card brand to use for authentication. Should be one of the brands returned in the additional_card_brands property when creating the session. |
Selecting a specific brand allows you to route the authentication through the preferred network, which may be beneficial for:
- Regional regulatory compliance (such as European PSD2 requirements)
- Cost optimization by choosing the most economical network for a transaction
- Customer preference for specific brand loyalty or rewards programs
If card_brand is not specified for a co-badged card, the default primary brand (returned in the card_brand property on session response) will be used.
Authentication Response
The authentication response contains everything you need to successfully validate a 3DS transaction or identify why it failed.
See below a detailed table with descriptions for what each field means, and continue reading to understand different authentication scenarios that can happen with a 3DS transaction.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
session_id | The id for the authenticated 3DS session |
threeds_version | The 3DS version (i.e. 2.2.0) used in the transaction |
token_id | The ID of the card token used in the 3DS transaction |
token_intent_id | The ID of the card token intent used in the 3DS transaction |
acs_transaction_id | The transaction ID from the 3DS Access Control Server (ACS) |
ds_transaction_id | The transaction ID from the 3DS Directory Server (DS) |
acs_reference_number | A unique identifier assigned to the DS by EMVCo |
ds_reference_number | A unique identifier assigned to the ACS by EMVCo |
authentication_value | The 3DS cryptogram value used to authorize the transaction. Also know as CAVV, AAV, AEVV, etc. |
authentication_status | The outcome of the 3DS authentication. See Authentication Scenarios |
authentication_status_code | EMVCo character code for the authentication status |
authentication_status_reason | Additional information about the authentication status if necessary. See Failed Authentication. Not provided on frictionless authentication |
authentication_status_reason_code | EMVCo numeric code for the authentication status reason. |
eci | Electronic Commerce Indicator (ECI) |
acs_challenge_mandated | Indicates whether regional mandates (e.g., PSD2) require a challenge to be performed |
authentication_challenge_type | The type of challenge authentication used (if challenge) |
acs_challenge_url | The URL to be used for the challenge |
challenge_preference | The selected Challenge Preference during authentication |
challenge_preference_code | EMVCo numeric code for the selected challenge preference |
challenge_attempts | The number of challenges attempted by the cardholder. Not provided on frictionless authentication |
challenge_cancel_reason | The reason why a challenge was cancelled. Not provided on frictionless authentication |
challenge_cancel_reason_code | EMVCo numeric code for the challenge cancel reason. Not provided on frictionless authentication |
cardholder_info | Unspecified information from the issuer to be displayed to the cardholder |
whitelist_status | Indicates if the cardholder whitelisted the merchant |
whitelist_status_source | Identifies the system that set the whitelist value |
message_extensions | Array of Message Extensions - Data necessary to support requirements not defined in the standard 3DS format |
Authentication Scenarios
Below are how to handle the scenarios that could be returned from the Authentication step. Generally, this will fall into he following scenarios:
| Authentication Scenarios | Statuses | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Frictionless | success, attempted | The authentication was approved by the issuer and the transaction may proceed. |
| Challenge | challenge | The issuer is requesting additional authentication before allowing the transaction to proceed. |
| Decoupled Challenge | decoupled_challenge | The issuer requires additional authentication to be performed outside of the transaction scope. |
| 3DS Failed | failed, unavailable, rejected | The 3DS authentication was not approved. Reason is provided in authentication_status_reason property. |
Frictionless Authentication
If the authentication_status indicates success, your authentication has been approved, and the response includes the authentication values needed to send to your Processor.
Note: The attempted status also produces a frictionless authentication. However, in this case, it indicates the ACS (Access Control Server) encountered an issue authenticating the transaction. From the merchant's perspective, it works like a success (no further authentication steps are required), although liability considerations may differ.
Challenge Authentication
If the authentication_status indicates a challenge, the cardholder must complete an additional verification step—a "Challenge"—before the 3DS authentication can be finalized and the final authentication value (CAVV) provided.
Challenges can vary significantly, often involving methods such as entering a one-time password (OTP) or authorizing the transaction via a banking app.
The presentation and completion method of the challenge are determined entirely by the issuer, and the merchant has no control over this process. See below how to use the Basis Theory 3DS SDKs to successfully start a Challenge.
- Web
- React Native
- iOS
- Android
import { BasisTheory3ds } from "@basis-theory/web-threeds";
const authenticate = async () => {
const bt3ds = BasisTheory3ds("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>");
// creating the session
// (in this example we are using tokenId for a card token, use tokenIntentId for a token intent)
const session = await bt3ds.createSession({ tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>" });
// ... backend code to authenticate the session and return the authentication response
// (in this example, we assume you received the authentication response in a variable called `authentication`)
if (authentication.authenticationStatus === 'challenge') {
// check casing for the payload to see if it matches with what your backend returned
const challengePayload = {
sessionId: session.id,
acsChallengeUrl: authentication.acs_challenge_url,
acsTransactionId: authentication.acs_transaction_id,
threeDSVersion: authentication.threeds_version,
}
// starting the challenge
// when user completes the challenge, the SDK will resolve the promise (or reject it in case of errors)
const challenge = await bt3ds.startChallenge(challengePayload);
}
}
import { BasisTheory3dsProvider, useBasisTheory3ds } from "@basis-theory/react-native-threeds";
const App = () => {
return (
<BasisTheory3dsProvider apiKey={"<PUBLIC_API_KEY>"}>
<MyApp />
</BasisTheory3dsProvider>
);
}
const MyApp = () => {
const { createSession, startChallenge } = useBasisTheory3ds();
//creating the session
// (in this example we are using tokenId for a card token, use tokenIntentId for a token intent)
const session = await createSession({ tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>" });
// ... backend code to authenticate the session and return the authentication response
// (in this example, we assume you received the authentication response in a variable called `authentication`)
if (authentication.status === "challenge") {
// check casing for the payload to see if it matches with what your backend returned
const challengePayload = {
sessionId: session.id,
acsChallengeUrl: authentication.acs_challenge_url,
acsTransactionId: authentication.acs_transaction_id,
threeDSVersion: authentication.threeds_version,
}
// starting a challenge
// when user completes the challenge, the SDK will resolve the promise (or reject it in case of errors)
const challengeCompleted = await startChallenge(challengeInfo);
}
}
import ThreeDS
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, UITextFieldDelegate {
private var threeDSService: ThreeDSService!
private var sessionId: String? = nil
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
do {
threeDSService = try ThreeDSService.builder()
.withApiKey("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>")
.withAuthenticationEndpoint("<YOUR_BACKEND_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT>", headers: ["Header-Name": "value"])
.build()
Task {
try await threeDSService.initialize { [weak self] warnings in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
if let warnings = warnings, !warnings.isEmpty {
let messages = warnings.map { $0.message }.joined(separator: "\n")
print(messages)
} else {
print("3DS SDK initialized successfully.")
}
}
}
}
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
// call this method from your app when you want to create a session
@objc func createThreeDsSession() {
Task {
do {
let session = try await self.threeDSService.createSession(tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>")
sessionId = session.id
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
}
// call this method from your app when you want to start a challenge
// (in this example, we assume your app received confirmation from your backend that a challenge is necessary)
@objc func startChallenge() {
Task {
do {
guard let sessionId = sessionId else {
throw ThreeDSError.missingSessionId
}
try await self.threeDSService.startChallenge(
sessionId: sessionId, viewController: self,
onCompleted: { result in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
print("Challenge completed with result: \(result)")
}
guard let details = result.details else {
return
}
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.detailsLabel.text = "\(details)"
}
},
onFailure: { result in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
print("Challenge failed with error: \(result)")
}
})
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
}
}
// ... other imports
import com.basistheory.threeds.service.ThreeDSService
import com.basistheory.threeds.model.CreateThreeDsSessionResponse
import com.basistheory.threeds.model.ChallengeResponse
open class ThreeDsViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
private val _errorMessage = MutableLiveData<String?>(null)
val errorMessage: LiveData<String?> = _errorMessage
val session = MutableLiveData<CreateThreeDsSessionResponse?>(null)
val challengeResponse = MutableLiveData<ChallengeResponse?>(null)
val status = MutableLiveData<String?>(null)
val statusReason = MutableLiveData<String?>(null)
private val threeDsService = ThreeDSService
.Builder()
.withApiKey("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>")
.withAuthenticationEndpoint("<YOUR_BACKEND_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT>")
.withApplicationContext(application.applicationContext)
.build()
fun initialize(): LiveData<List<String>> = liveData {
try {
val warnings = threeDsService.initialize()
if (!warnings.isNullOrEmpty()) {
emit(warnings.map { it.message })
} else {
emit(emptyList())
}
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(emptyList())
}
}
fun createSession(tokenId: String): LiveData<CreateThreeDsSessionResponse?> = liveData {
try {
session.value = threeDsService.createSession(tokenId = tokenId)
emit(session.value)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(null)
}
}
private fun onChallengeCompleted(result: ChallengeResponse) {
challengeResponse.postValue(result)
status.postValue(result.status)
result.details?.let {
statusReason.postValue(it)
}
}
private fun onChallengeFailed(result: ChallengeResponse) {
_errorMessage.postValue(result.toString())
}
// call this method from your app when you want to start a challenge
// (in this example, we assume your app received confirmation from your backend that a challenge is necessary)
fun startChallenge(sessionId: String, activity: Activity): LiveData<Boolean> = liveData {
_errorMessage.value = null
try {
threeDsService.startChallenge(
sessionId = sessionId,
activity = activity,
onCompleted = ::onChallengeCompleted,
onFailed = ::onChallengeFailed
)
emit(true)
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(false)
}
}
}
Verifying Challenge Completion
This section refers strictly to the customer's having finished the Challenge process, not to the success or failure of the authentication. To verify the challenge's outcome (success or failure), refer to the Getting a Challenge Result section.
The most common approach to receiving a Challenge Completion is via the front-end - awaiting the resolution of the SDK's challenge method or promise. Refer to the instructions for your specific Basis Theory 3DS SDK to see how to handle the challenge completion.
Alternatively, you can use our Webhooks solution. Subscribing a webhook to the 3ds.session.challenge-completed event will trigger when a challenge completion has finished and contain the id to enable Getting a Challenge Result.
Refer to our API documentation for details on setting up Webhooks and additional event properties.
Getting a Challenge Result
Once a challenge is completed, you must retrieve the result directly from the API. This step is essential to determining the challenge's outcome (success or failure) and obtaining the necessary authentication values (e.g., CAVV, ECI) for successfully authenticated transactions.
- cURL
- Node
- .NET
- Python
- Go
curl "https://api.test.basistheory.com/3ds/sessions/<SESSION_ID>/challenge-result" \
-H "BT-API-KEY: <PRIVATE_API_KEY>"
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK and Express framework for Node.js.
const express = require("express");
const { BasisTheoryClient } = require("@basis-theory/node-sdk")
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
app.use(express.json());
let bt;
(async () => {
// initialize the SDK
bt = await new BasisTheoryClient({ apiKey: "<PRIVATE_API_KEY>", environment: BasisTheoryEnvironment.Test });
// start the server (after SDK is initialized so we don't drop any requests
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://localhost:${PORT}`);
});
})();
app.post("/:sessionId/authenticate", async (req, res) => {
const { sessionId } = req.params;
try {
const authentication = await bt.threeds.sessions.authenticate(sessionId, {
authenticationCategory: "payment",
authenticationType: "payment-transaction",
challengePreference: "no-challenge",
merchantInfo: {
mid: "9876543210001",
acquirerBin: "000000999",
name: "Example 3DS Merchant",
categoryCode: "7922",
countryCode: "826",
url: "https://example.com",
},
requestorInfo: { // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
amexRequestorType: "MER", // if American Express is accepted
cbSiretNumber: "78467169500087", // if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
},
purchaseInfo: {
amount: "80000",
currency: "826",
exponent: "2",
date: "20240109141010",
transactionType: "purchase",
//installmentCount": "5", // only for installment transactions
//recurringExpiration: "20250131", // only for recurring transactions
//recurringFrequency: "30", // only for recurring transactions
},
cardholderInfo: {
name: "John Doe",
email: "john@example.com"
}
});
res.status(200).send(authentication);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error during authentication:', error);
res.status(500).send({ error: "Internal Server Error" });
}
});
app.get("/:sessionId/challenge-result", async (req, res) => {
const { sessionId } = req.params;
try {
const result = await bt.threeds.sessions.getChallengeResult(sessionId);
if (!result) {
return res.status(500).send({ error: "Failed to get challenge result." });
}
res.status(200).send(result);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error getting challenge result:', error);
res.status(500).send({ error: "Internal Server Error" });
}
});
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK and ASP.NET Core Framework.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using BasisTheory.Client;
using BasisTheory.Client.Threeds;
namespace server.Controllers
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.UseUrls("http://0.0.0.0:4242")
.UseWebRoot("public")
.UseStartup<Startup>()
.Build()
.Run();
}
}
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc().AddNewtonsoftJson();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment()) app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
app.UseRouting();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints => endpoints.MapControllers());
}
}
[ApiController]
public class ThreeDsApiController : Controller
{
private readonly BasisTheory _client;
public ThreeDsApiController()
{
_client = new BasisTheory(apiKey: "<PRIVATE_API_KEY>");
}
[HttpPost("{sessionId:guid}/authenticate")]
public async Task<ActionResult> AuthenticateSession([FromRoute] Guid sessionId)
{
try
{
var authentication = await _client.Threeds.Sessions.AuthenticateAsync(sessionId.ToString(), new AuthenticateThreeDsSessionRequest
{
AuthenticationCategory = "payment",
AuthenticationType = "payment-transaction",
ChallengePreference = "no-challenge",
MerchantInfo = new ThreeDsMerchantInfo
{
Mid = "9876543210001",
AcquirerBin = "000000999",
Name = "Example 3DS Merchant",
CategoryCode = "7922",
CountryCode = "826",
Url = "https://example.com"
},
RequestorInfo = new ThreeDsRequestorInfo // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
{
AmexRequestorType = "MER", // if American Express is accepted
CbSiretNumber = "78467169500087" // if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
},
PurchaseInfo = new ThreeDsPurchaseInfo
{
Amount = "80000",
Currency = "826",
Exponent = "2",
Date = "20240109141010",
TransactionType = "purchase",
// InstallmentCount = "5", // only for installment transactions
// RecurringExpiration = "20250131", // only for recurring transactions
// RecurringFrequency = "30", // only for recurring transactions
},
CardholderInfo = new ThreeDsCardholderInfo
{
Name = "John Doe",
Email = "john@example.com"
}
});
if (authentication == null)
{
return Problem("Error during authentication.");
}
return Ok(authentication);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error during authentication: {ex.Message}");
return Problem("Internal Server Error");
}
}
[HttpGet("{sessionId:guid}/challenge-result")]
public async Task<ActionResult> GetChallengeResult([FromRoute] Guid sessionId)
{
try {
var result = await _client.Threeds.Sessions.GetChallengeResultAsync(sessionId.ToString());
if (result == null)
{
return Problem("Failed to get challenge result.");
}
return Ok(result);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Error getting challenge result: {ex.Message}");
return Problem("Internal Server Error");
}
}
}
}
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK and Flask Framework.
import os
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from basis_theory import (
BasisTheory,
ThreeDsMerchantInfo,
ThreeDsRequestorInfo,
ThreeDsPurchaseInfo,
ThreeDsCardholderInfo
)
app = Flask(__name__)
client = BasisTheory(api_key="<PRIVATE_API_KEY>")
@app.route('/<sessionId>/authenticate', methods=['POST'])
def authenticate_session(sessionId):
try:
authentication = client.threeds.sessions.authenticate(
session_id=sessionId,
authentication_category="payment",
authentication_type="payment-transaction",
challenge_preference="no-challenge",
merchant_info=ThreeDsMerchantInfo(
mid="9876543210001",
acquirer_bin="000000999",
name="Example 3DS Merchant",
category_code="7922",
country_code="826",
url="https://example.com"
),
requestor_info=ThreeDsRequestorInfo( # if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
amex_requestor_type="MER", # if American Express is accepted
cb_siret_number="78467169500087" # if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
),
purchase_info=ThreeDsPurchaseInfo(
amount="80000",
currency="826",
exponent="2",
date="20240109141010",
transaction_type="purchase",
# installment_count="5", # only for installment transactions
# recurring_expiration="20250131", # only for recurring transactions
# recurring_frequency="30", # only for recurring transactions
),
cardholder_info=ThreeDsCardholderInfo(
name="John Doe",
email="john@example.com"
)
)
if authentication is None:
return jsonify({"error": "Error during authentication."}), 500
return jsonify(authentication.to_dict()), 200
except Exception as ex:
print(f"Error during authentication: {ex}")
return jsonify({"error": "Internal Server Error"}), 500
@app.route('/<sessionId>/challenge-result', methods=['GET'])
def get_challenge_result(sessionId):
try:
result = client.threeds.sessions.get_challenge_result(sessionId)
if result is None:
return jsonify({"error": "Failed to get challenge result."}), 500
return jsonify(result.to_dict()), 200
except Exception as ex:
print(f"Error getting challenge result: {ex}")
return jsonify({"error": "Internal Server Error"}), 500
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(port=4242, debug=True)
In this example, we are using Basis Theory SDK, Go HTTP package and the Gorilla Mux Router.
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk"
basistheoryclient "github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/client"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/option"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/threeds"
"github.com/gorilla/mux"
"log"
"net/http"
)
var client *basistheoryclient.Client
func main() {
client := basistheoryclient.NewClient(
option.WithAPIKey("<API_KEY>"),
)
router := mux.NewRouter()
router.HandleFunc("/{sessionId}/authenticate", authenticateSession).Methods("POST")
router.HandleFunc("/{sessionId}/challenge-result", getChallengeResult).Methods("GET")
addr := "localhost:4242"
log.Printf("Listening on %s", addr)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe(addr, router))
}
func pointerToString(s string) *string {
return &s
}
func authenticateSession(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
sessionId := vars["sessionId"]
authRequest := &threeds.AuthenticateThreeDsSessionRequest{
AuthenticationCategory: "payment",
AuthenticationType: "payment-transaction",
ChallengePreference: "no-challenge",
}
merchantInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsMerchantInfo{
Mid: pointerToString("9876543210001"),
AcquirerBin: pointerToString("000000999"),
Name: pointerToString("Example 3DS Merchant"),
CategoryCode: pointerToString("7922"),
CountryCode: pointerToString("826"),
Url: pointerToString("https://example.com"),
}
requestorInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsRequestorInfo{ // if accepting American Express, Discover or Cartes Bancaires
AmexRequestorType: pointerToString("MER"), // if American Express is accepted
CbSiretNumber: pointerToString("78467169500087"), // if Cartes Bancaires is accepted
}
purchaseInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsPurchaseInfo{
Amount: pointerToString("80000"),
Currency: pointerToString("826"),
Exponent: pointerToString("2"),
Date: pointerToString("20240109141010"),
TransactionType: pointerToString("purchase"),
// InstallmentCount: pointerToString("5"), // only for installment transactions
// RecurringExpiration: pointerToString("20250131"), // only for recurring transactions
// RecurringFrequency: pointerToString("30"), // only for recurring transactions
}
cardholderInfo := &basistheory.ThreeDsCardholderInfo{
Name: pointerToString("John Doe"),
Email: pointerToString("john@example.com"),
}
authRequest.MerchantInfo = merchantInfo
authRequest.RequestorInfo = requestorInfo
authRequest.PurchaseInfo = purchaseInfo
authRequest.CardholderInfo = cardholderInfo
authenticateResponse, authenticateErr := client.Threeds.Sessions.Authenticate(context.Background(), sessionId, authRequest)
if authenticateErr != nil {
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
json.NewEncoder(rw).Encode(map[string]string{"error": authenticateErr.Error()})
return
}
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
json.NewEncoder(rw).Encode(authenticateResponse)
}
func getChallengeResult(rw http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
vars := mux.Vars(r)
sessionId := vars["sessionId"]
result, err := client.Threeds.Sessions.GetChallengeResult(context.Background(), sessionId)
if err != nil {
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
json.NewEncoder(rw).Encode(map[string]string{"error": err.Error()})
return
}
rw.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
json.NewEncoder(rw).Encode(result)
}
Decoupled Challenge Authentication
Decoupled Challenge Authentication is a 3DS method that separates cardholder authentication from the payment flow, allowing the issuer to handle authentication without direct cardholder interaction at the time of the transaction.
This approach is more common in Merchant-Initiated Transactions (MIT) but possible in cases where the cardholder's device cannot support a typical challenge flow during a CIT.
Since this authentication occurs outside the immediate transaction flow, you must subscribe to the 3ds.session.decoupled-challenge-notification event via Webhooks to confirm when the authentication is complete.
Failed Authentication
A 3DS authentication may fail for various reasons, ranging from technical issues to rejections triggered by fraud or risk concerns. When you encounter a failed, unavailable, or rejected authentication_status, refer to the authentication_status_reason property to understand why the authentication did not succeed.
Depending on the reason, you can either:
- Retry the 3DS authentication using the same information.
- Adjust the authentication request (e.g., providing more details) before retrying.
The following table outlines possible authentication_status_reason values and recommended actions.
| Authentication Status Reason | Recommended Action |
|---|---|
low-confidencemedium-confidencehigh-confidencevery-high-confidenceauthentication-attempted-but-not-performedidentity-check-insights | The authentication was successful even though it failed, use authentication results returned with payment. |
invalid-transactiontransaction-not-permittedcardholder-not-enrollednon-payment-transaction-not-support3ri-not-supportedvmid-not-eligible-for-requested-programprotocol-version-not-supported-by-acs | Attempt payment without 3DS authentication. |
card-authentication-failedtoo-many-authentication-attemptscard-expiredinvalid-card-numberno-card-recordsecurity-failurestolen-cardsuspected-fraud | Inform consumer to use a different card or double-check details. |
unknown-deviceunsupported-device | Inform consumer to use a different device. |
timeout-at-acsmax-challenges-exceededacs-technical-issuedecoupled-authentication-requireddecoupled-authentication-timeoutinsufficient-decoupled-authentication-timeerror-connecting-to-acsacs-timed-outinvalid-response-from-acssystem-error-response-from-acsinternal-error-while-generating-cavvdevice-3ri-not-routed-to-smart-authentication-stand-intransaction-excluded-from-attempts-processing | Retry authentication. |
Refer to our API documentation for details on what each reason code means specifically.
Testing Basis Theory 3DS
Basis Theory Test Tenants automatically connect to the sandbox environment for testing your 3DS implementation.
This environment allows you to simulate the 3DS authentication flow without real-world impacts safely. To utilize 3DS in your Test Tenant, ensure 3DS has been enabled in your Tenant Quotas.
To guarantee a predictable and deterministic pattern for both automated and manual testing, a set of Test Cards exists to simulate different Authentication outcomes, helping validate various scenarios effectively.
Test Cards
Below is a list of Luhn-valid test cards that can be used to simulate different authentication scenarios in the sandbox environment. These cards are not real and will not work for testing in production environments.
| Card Number | Card Brand | Testing Scenario |
|---|---|---|
5204247750001471 | MASTERCARD | Successful Frictionless Authentication |
6011601160116011 | DISCOVER | Successful Frictionless Authentication |
340000000004001 | AMEX | Successful Frictionless Authentication |
4000020000000000 | VISA | Successful Challenge Authentication |
370000000000002 | AMEX | Successful Challenge Authentication |
3566002020360505 | JCB | Successful Challenge Authentication |
3566006663297692 | JCB | Successful Challenge Authentication |
4005562231212123 | VISA | Successful Challenge Authentication - Method not Required |
4761369980320253 | VISA | Successful Mandated Challenge Authentication |
5200000000001104 | MASTERCARD | Successful Mandated Challenge Authentication |
4000000000000341 | VISA | Successful Out-of-Band Challenge Authentication |
4005571701111111 | VISA | Attempted Challenge Authentication |
4111111111111111 | VISA | Authentication Attempted |
5424180011113336 | MASTERCARD | Authentication Attempted |
4264281511112228 | VISA | Authentication Failed |
5424180000000171 | MASTERCARD | Authentication Failed |
5405001111111165 | MASTERCARD | Authentication Unavailable |
5405001111111116 | MASTERCARD | Authentication Rejected |
4055011111111111 | VISA | Failed Challenge Authentication |
5427660064241339 | MASTERCARD | Failed Challenge Authentication |
6011361011110004 | DISCOVER | Failed Out of Band Challenge Authentication |
6011361000008888 | DISCOVER | Unavailable Challenge Authentication |
6011361000001115 | DISCOVER | Rejected Challenge Authentication |
4264281500003339 | VISA | 3DS Directory Server Error |
5424180011110001 | MASTERCARD | 3DS Directory Server Error |
4264281500001119 | VISA | Internal 3DS Server Error |
4150580996517927 | VISA, CARTES BANCAIRES | Co-Badged Card - Successful Challenge Authentication |
4150580996517927 | MASTERCARD, CARTES BANCAIRES | Co-Badged Card - Successful Challenge Authentication |
Error Handling
Proper error handling is crucial for delivering a smooth user experience when implementing 3DS authentication. There are two primary categories of errors you'll encounter:
- Basis Theory API Errors - Standard Basis Theory API errors (e.g., invalid API keys, validation errors).
- 3DS Service Errors - Errors from the 3DS Server, Directory Server, or Access Control Server.
Handling 3DS Service Errors
3DS Service Errors occur when issues arise during the external 3DS authentication process.
These errors are returned with a 424 HTTP status code, providing detailed information on the failure:
{
"error": {
"title": "3DS Service Error",
"detail": "The 3DS service returned an error. See the 'error' field for more details.",
"status": 424,
"error": {
"service_status": "403",
"session_id": "c0c22fcd-d42c-497e-a9a6-2eacd31770d7",
"error_source": "3DS Server",
"message": "Access denied by issuer. See 'details' for additional detail.",
"detail": "The merchant_info.acquirer_bin is not recognized by the issuer."
}
}
}
The error object will contain all the necessary details on what the error was and how to handle it.
Below are some suggestions on how to handle common errors based on the received error.service_status code.
| Service Status | Error Scenario | Possible Actions |
|---|---|---|
400 | Bad Request | Check the request payload and ensure it's correct. Details are included in the message and detail fields. |
401, 403 | Access Denied | Check your merchant information (MID, Acquirer BIN, etc.) and ensure it's correct for the card network you're using. |
404 | Not Found | Check if the session ID is correct and that the session exists in the tenant. |
5XX | Internal Service Errors | Check the error message and if applicable, retry the authentication. For 502 and 504, the transaction must be fully retried by creating a new session. |
If you have questions about specific error codes or how to handle them, please reach out to our support team at support@basistheory.com.
You can find below examples of how to handle 3DS Service Errors using the backend SDKs.
- Node
- .NET
- Python
- Go
import { BasisTheoryClient, BasisTheoryError } from "@basis-theory/node-sdk";
try {
const authentication = await bt.threeds.sessions.authenticate(sessionId, {
authenticationCategory: "payment",
authenticationType: "payment-transaction",
// ... other properties
});
// ... handle successful authentication
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof BasisTheoryError) {
const statusCode = error.statusCode;
if (statusCode === 424) {
// handle specific 3DS service error
const serviceError = JSON.parse(error.body).error;
console.error("Error Message:", serviceError.message);
console.error("Details:", serviceError.detail);
console.error("Service Status:", serviceError.service_status);
console.error("Error Source:", serviceError.error_source);
console.error("Session ID:", serviceError.session_id);
} else {
// handle other Basis Theory API errors
console.error("Basis Theory API Error:", error.message);
}
} else {
// handle unknown errors
console.error("Unexpected Error:", error);
}
}
using BasisTheory.Client;
using BasisTheory.Client.Threeds;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
var client = new BasisTheory.Client.BasisTheory(apiKey: "<PRIVATE_API_KEY>");
try
{
var authentication = await client.Threeds.Sessions.AuthenticateAsync(sessionId.ToString(), new AuthenticateThreeDsSessionRequest
{
AuthenticationCategory = "payment",
AuthenticationType = "payment-transaction",
// ... other properties
});
// ... handle successful authentication
}
catch (BasisTheoryApiException e)
{
if (e.StatusCode == 424)
{
// handle specific 3DS service error
var errorJson = JObject.Parse(e.Body);
var serviceError = errorJson["error"];
Console.WriteLine("3DS Service Error:");
Console.WriteLine($"Message: {serviceError["message"]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Detail: {serviceError["detail"]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Service Status: {serviceError["service_status"]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Error Source: {serviceError["error_source"]}");
Console.WriteLine($"Session ID: {serviceError["session_id"]}");
}
else
{
// handle other Basis Theory API errors
Console.WriteLine($"Basis Theory API Error: {e.Message} (Status: {e.StatusCode})");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// handle unknown errors
Console.WriteLine($"Unexpected Error: {ex.Message}");
}
from basis_theory import BasisTheory
from basis_theory.core.api_error import ApiError
import json
client = BasisTheory(api_key="<PRIVATE_API_KEY>")
try:
authentication = client.threeds.sessions.authenticate(
session_id=sessionId,
authentication_category="payment",
authentication_type="payment-transaction",
# ... other properties
)
# ... handle successful authentication
except ApiError as e:
if e.status_code == 424:
# handle specific 3DS service error
error_body = json.loads(e.body)
service_error = error_body.get("error", {})
print("3DS Service Error:")
print(f"Message: {service_error.get('message')}")
print(f"Detail: {service_error.get('detail')}")
print(f"Service Status: {service_error.get('service_status')}")
print(f"Error Source: {service_error.get('error_source')}")
print(f"Session ID: {service_error.get('session_id')}")
else:
# handle other Basis Theory API errors
print(f"Basis Theory API Error: {e.body} (Status: {e.status_code})")
except Exception as ex:
# handle unknown errors
print(f"Unexpected Error: {ex}")
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/client"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/core"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/option"
"github.com/Basis-Theory/go-sdk/threeds"
)
func main() {
btClient := client.NewClient(
option.WithAPIKey("<PRIVATE_API_KEY>"),
)
sessionId := "<SESSION_ID>"
authRequest := &threeds.AuthenticateThreeDsSessionRequest{
AuthenticationCategory: "payment",
AuthenticationType: "payment-transaction",
// ... other properties
}
authResponse, err := btClient.Threeds.Sessions.Authenticate(context.Background(), sessionId, authRequest)
if err != nil {
if apiErr, ok := err.(*core.APIError); ok {
if apiErr.StatusCode == 424 {
var errorDetails map[string]interface{}
// Use apiErr.Error() which returns the error message (body included)
if jsonErr := json.Unmarshal([]byte(apiErr.Unwrap().Error()), &errorDetails); jsonErr == nil {
if svcErr, exists := errorDetails["error"].(map[string]interface{}); exists {
fmt.Println("3DS Service Error:")
fmt.Printf("Message: %v\n", svcErr["message"])
fmt.Printf("Detail: %v\n", svcErr["detail"])
fmt.Printf("Service Status: %v\n", svcErr["service_status"])
fmt.Printf("Error Source: %v\n", svcErr["error_source"])
fmt.Printf("Session ID: %v\n", svcErr["session_id"])
} else {
fmt.Println("Unable to parse detailed error fields.")
}
} else {
fmt.Printf("Error decoding JSON: %v\n", jsonErr)
}
} else {
fmt.Printf("Basis Theory API Error (Status: %d): %v\n", apiErr.StatusCode, apiErr.Error())
}
} else {
fmt.Printf("Unexpected error: %v\n", err)
}
return
}
// ... handle successful authentication
}
Handling Errors in Frontend SDKs
When using the Basis Theory 3DS SDKs, errors are handled through the SDK's built-in error handling mechanisms.
The SDK will throw exceptions or return error objects that you can catch and handle in your application. See below examples on how to handle with our current SDKs.
- Web
- React Native
- iOS
- Android
import { BasisTheory3ds } from "@basis-theory/web-threeds";
const authenticate = async () => {
const bt3ds = BasisTheory3ds("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>");
try {
const session = await bt3ds.createSession({ tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>" });
} catch (error) {
// handle error
console.error("Error creating session:", error);
return;
}
}
import { BasisTheory3dsProvider, useBasisTheory3ds } from "@basis-theory/react-native-threeds";
const App = () => {
return (
<BasisTheory3dsProvider apiKey={"<PUBLIC_API_KEY>"}>
<MyApp />
</BasisTheory3dsProvider>
);
}
const MyApp = () => {
const { createSession, startChallenge } = useBasisTheory3ds();
try {
const session = await createSession({ tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>" });
// ... handle successful session creation
} catch (error) {
// handle error
console.error("Error creating session:", error);
return;
}
}
import ThreeDS
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController, UITextFieldDelegate {
private var threeDSService: ThreeDSService!
private var sessionId: String? = nil
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
do {
threeDSService = try ThreeDSService.builder()
.withApiKey("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>")
.withAuthenticationEndpoint("<YOUR_BACKEND_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT>", headers: ["Header-Name": "value"])
.build()
Task {
try await threeDSService.initialize { [weak self] warnings in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
if let warnings = warnings, !warnings.isEmpty {
let messages = warnings.map { $0.message }.joined(separator: "\n")
print(messages)
} else {
print("3DS SDK initialized successfully.")
}
}
}
}
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
// call this method from your app when you want to create a session
@objc func createThreeDsSession() {
Task {
do {
let session = try await self.threeDSService.createSession(tokenId: "<CARD_TOKEN_ID>")
sessionId = session.id
// ... handle successful session creation
} catch {
// handle error
}
}
}
}
// ... other imports
import com.basistheory.threeds.service.ThreeDSService
import com.basistheory.threeds.model.CreateThreeDsSessionResponse
open class ThreeDsViewModel(application: Application) : AndroidViewModel(application) {
private val _errorMessage = MutableLiveData<String?>(null)
val errorMessage: LiveData<String?> = _errorMessage
val session = MutableLiveData<CreateThreeDsSessionResponse?>(null)
private val threeDsService = ThreeDSService
.Builder()
.withApiKey("<PUBLIC_API_KEY>")
.withAuthenticationEndpoint("<YOUR_BACKEND_AUTHENTICATION_ENDPOINT>")
.withApplicationContext(application.applicationContext)
.build()
fun initialize(): LiveData<List<String>> = liveData {
try {
val warnings = threeDsService.initialize()
if (!warnings.isNullOrEmpty()) {
emit(warnings.map { it.message })
} else {
emit(emptyList())
}
} catch (e: Throwable) {
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(emptyList())
}
}
fun createSession(tokenId: String): LiveData<CreateThreeDsSessionResponse?> = liveData {
try {
session.value = threeDsService.createSession(tokenId = tokenId)
emit(session.value)
// ... handle successful session creation
} catch (e: Throwable) {
// handle error
_errorMessage.postValue(e.message)
emit(null)
}
}
}
3DS Implementation FAQs
What is a Basis Theory 3DS Session?
A Basis Theory 3DS Session represents the lifecycle of a 3DS authentication process.
It stores transaction details and dynamically captures data as each step of the authentication flow is completed, providing a complete record of the transaction's 3DS authentication journey.
What's the difference between this implementation and the redirect approach?
This guide covers the standard 3DS CIT implementation where:
- The authentication flow is embedded directly in your checkout page
- You use Basis Theory SDKs to handle device data collection and challenges
- You have full control over the user experience and styling
The 3DS CIT with Redirection approach is where:
- The 3DS session is created from your backend with all authentication details upfront
- Customers are redirected to the Basis Theory 3DS authentication page
- Basis Theory handles the entire authentication flow and redirects customers back to your site
- Less customization but simpler implementation
Choose the redirect approach if you want simpler implementation and don't need to customize the authentication experience. Choose this standard approach if you want full control over the user experience.
Can I create a CIT 3DS Session without using Basis Theory SDKs?
For native mobile applications (iOS and Android), you must use Basis Theory's SDK due to specific device data collection and security requirements.
For Web or React Native applications, creating a 3DS session manually via the API is technically possible but not recommended, as it involves manually managing device/browser data capture and handling the Method Request.
If you prefer to implement this, refer to our API reference on session creation.
How long is a 3DS Session kept in the Basis Theory vault?
When a 3DS session is created, its expiration date inherits that of the token or token-intent used. The session defaults to a one-hour expiration if no expiration date is present.
However, once the session is authenticated, it no longer expires and remains stored indefinitely—provided your tenant remains active.
How can I retrieve a 3DS Session to see its details?
Use the Get Session endpoint, ensuring you include a private application key with the 3ds:session:read permission.
Are there limits on the number of 3DS sessions I can create?
No. There are currently no restrictions on how many 3DS sessions you can create for the same token, token-intent or in general.
You're free to create as many as you need for testing or operational purposes.
What authentication_category should I use in most authentication scenarios?
In the majority of cases, including both current or future charges, set the authentication_category to payment.
What authentication_type should I use in most authentication scenarios?
For most single-purchase or one-time payment scenarios, use the purchase-transaction.
For recurring transactions where the same amount is charged each month, use recurring-transaction.
For installment transactions where a product is broken into multiple payments, use installment-transaction
What settings do I use if I only do a $0 Authorization?
Yes, when doing pre-authorizations, that signifies the intent to charge - you should use payment as the authentication_category and purchase as the authentication_type.
How do I find my Merchant Information?
Your Payment Service Provider (PSP) is responsible for providing these details.
Refer to our Setup Guide for specific instructions on communicating your requirements and ensuring your PSP gives you the necessary merchant data.
Can I store my Merchant Information with Basis Theory so I don't have to include it in every authentication request?
At the moment, you must provide this information with each request. However, Basis Theory is actively developing a solution that will allow you to store these values and automatically populate them on future 3DS requests.
I support AMEX, what value should I use as the requestor_info.amex_requestor_type?
If you are a merchant or are processing for a Merchant, you will usually set requestor_info.amex_requestor_type to MER.
If your organization fits a different category (e.g., aggregator, online travel agency), refer to the available AMEX requestor types in our Setup Guide or consult your PSP.
How does a recurring or installment transaction work? Do I need to repeat 3DS authentication for each additional charge?
When processing recurring or installment transactions using 3DS, we recommend performing an initial Cardholder-Initiated Transaction (CIT) authentication, ensuring you include the appropriate recurring or installment details.
Typically, subsequent recurring or installment payments do not require additional 3DS authentications. However, it's best practice to confirm with your PSP if they have additional requirements or guidelines.
If your PSP indicates that additional authentications are needed for subsequent payments, you can reuse the authentication value from the initial CIT authentication or perform a new 3DS authentication while including the prior authentication information.
This approach helps ensure frictionless authentications for ongoing payments.
What information about the cardholder do I need to provide?
Most card networks require, at a minimum, the cardholder's name and email address.
Providing additional details (such as billing address or phone number) can help improve authentication success rates, especially if you experience lower-than-expected approval rates.
Refer to the Taking 3DS Live Guide for further recommendations.
Will my set Challenge Preference always be respected by the issuer?
No. The challenge_preference you set is only a suggestion. The issuer decides whether to prompt a challenge based on its risk assessment and compliance requirements.
What is a frictionless 3DS authentication?
A frictionless 3DS authentication is a successful authentication where no challenge was required.
How can I verify a non-frictionless challenge was completed?
You can either wait for the SDKs challenge methods promises to be completed or use the 3ds.session.challenge-completed webhook.
How do I handle co-badged cards in 3DS authentication?
When creating a 3DS session for a co-badged card (a card associated with multiple networks), the response will include an additionalCardBrands array listing all brands the card supports.
During authentication, you can specify which brand to use by including the card_brand parameter with the desired brand name. This allows you to route the authentication through your preferred network based on considerations like regional regulations, costs, or customer preferences.
If no card_brand is specified, the authentication will default to the primary card brand (the first one in the additionalCardBrands array).
Is it possible to detect when a user cancels a challenge in real time?
No. To confirm that a user has canceled a challenge, you must retrieve the challenge result via the Get a Challenge Result endpoint.
The response will include a challenge_cancel_reason, indicating that the user explicitly canceled the challenge.
How can I retrieve the authentication values of a completed challenge?
You should use the Get Challenge Result endpoint to get the results of a challenge.
Is it possible for CITs to have decoupled challenges?
Yes. Although decoupled challenges are more commonly used in Merchant-Initiated Transactions (MITs), they can occur in Customer-Initiated Transactions (CITs) as well—particularly if the cardholder's device doesn't support the standard challenge flow.
Is it possible to style the way a challenge window looks?
The issuer or acquirer fully controls the design and layout of the challenge window (e.g., fonts and colors).
However, Basis Theory allows you to customize the size and placement of the challenge window in your application.
Refer to the SDK documentation for platform-specific instructions.
Does Basis Theory provide a way to test a 3DS implementation?
Yes, 3DS authentications from a Test Tenant will use our 3DS Sandbox environment. For more details, refer to the Testing session in this guide.
Does Basis Theory provide test cards for use in the testing environment?
Yes, refer to the Test Cards session in this guide.
Why do I see a 'ACS browser fingerprinting FAILED!' message in the browser console when creating a session in the test environment?
That message can be safely ignored as it only exists for internal test scenarios
Does Basis Theory provide test cards for use in a production environment?
No. You must use your real cards or request production-ready test cards from your PSP.
Basis Theory does not support test scenarios in production; any card used in a production tenant will undergo a live 3DS authentication with real data.
Can I test a 3DS implementation End-to-End(E2E) between Basis Theory and my PSP?
There are a few options for how to test implementations in Test and Production Tenants.
For Test Tenants: The nature of standalone 3DS typically prevents fully end-to-end payment tests in a sandbox environment because Basis Theory and the PSP each have separate test data sets.
- To test 3DS scenarios, Use Basis Theory's 3DS Test Cards.
- To test the PSP authorization with 3DS data: Follow your PSP's testing guidelines. This often involves using their specific test cards and dummy 3DS values.
For Production Tenants: You can utilize your real-life cards to test the implementation fully end to end with Basis Theory and all of your PSPs.